The Stillwater Mining Co. Minn.Adit Prj is a pge, platinum, and palladium mine located in Stillwater county, Montana at an elevation of 5,249 feet.
About the MRDS Data:
All mine locations were obtained from the USGS Mineral Resources Data System. The locations and other information in this database have not been verified for accuracy. It should be assumed that all mines are on private property.
Mine Info
Elevation: 5,249 Feet (1,600 Meters)
Commodity: PGE, Platinum, Palladium
Lat, Long: 45.3878, -109.87920
Map: View on Google Maps
Satelite View
MRDS mine locations are often very general, and in some cases are incorrect. Some mine remains have been covered or removed by modern industrial activity or by development of things like housing. The satellite view offers a quick glimpse as to whether the MRDS location corresponds to visible mine remains.
Stillwater Mining Co. Minn.Adit Prj MRDS details
Site Name
Primary: Stillwater Mining Co. Minn.Adit Prj
Secondary: J-M Reef Deposit
Secondary: Minneapolis Adit Project
Secondary: Stillwater Mine
Secondary: Johns-Manville Stillwater Platinum
Secondary: Stillwater Platinum Project
Secondary: Stillwater Pgm Resources
Secondary: M Prospect
Commodity
Primary: PGE
Primary: Platinum
Primary: Palladium
Secondary: Gold
Secondary: Rhodium
Tertiary: Osmium
Tertiary: Iridium
Tertiary: Nickel
Tertiary: Copper
Tertiary: Ruthenium
Location
State: Montana
County: Stillwater
District: Stillwater
Land Status
Land ownership: National Forest
Note: the land ownership field only identifies whether the area the mine is in is generally on public lands like Forest Service or BLM land, or if it is in an area that is generally private property. It does not definitively identify property status, nor does it indicate claim status or whether an area is open to prospecting. Always respect private property.
Holdings
Type: Patented
Type: Located Claim
Workings
Not available
Ownership
Owner Name: Johns-Manville Products Corp.
Company ID: 2401490
Percent: 50.00
Info Year: 1990
Years: 1979 - 1994
Owner Name: Stillwater PGM Resources
Info Year: 1998
Years: 1979 - 1994
Owner Name: Chevron Resources, Inc.
Company ID: 2401490
Percent: 50.00
Info Year: 1990
Years: 1979 - 1994
Owner Name: Stillwater Mining Co.
Company ID: 2401490
Percent: 100.0
Home Office: Montana
Info Year: 1996
Years: 1994 -
Production
Year: 1995
Description: Palladium Production 169000 Troy Ounces
Year: 1995
Description: Platinum Production 51000 Troy Ounces
Deposit
Record Type: Site
Operation Category: Producer
Deposit Type: PGE Reef
Plant Type: Beneficiation (Mill)
Plant Subtype: Flotation
Operation Type: Underground
Mining Method: Filled Stopes - Horiz Cut and Fill W/Waste Rock
Milling Method: Flotation
Year First Production: 1986
Discovery Year: 1971
Years of Production:
Organization:
Significant: Y
Physiography
General Physiographic Area: Rocky Mountain System
Physiographic Province: Middle Rocky Mountains
Mineral Deposit Model
Model Name: Merensky Reef PGE
Orebody
Name: J-M Reef
Form: Tabular, stratiform, disseminated
Structure
Type: L
Structure: Faults
Type: L
Structure: Folds
Type: L
Structure: High-Angle Reverse Faults
Alterations
Not available
Rocks
Not available
Analytical Data
Analytical Data: HOST ROCKS CONTAIN 0.5-1.0% CHALCOPYRITE+PYRRHOTITE+PENTLANDITE WHICH CONTAIN SMALL AMOUNTS OF PLATINUM BEARING SULFIDES. ONE 5.5 KM SEGMENT OF REEF AVERAGES 22.3PPM PT+PD OVER 2.1 M WIDTH. PT:PD=1:3.
Materials
Ore: Pyrite
Ore: Gold
Ore: Chalcopyrite
Ore: Pentlandite
Ore: Pyrrhotite
Ore: Mackinawite
Ore: Platinum
Ore: Palladium
Gangue: Plagioclase
Gangue: Tremolite
Gangue: Hornblende
Gangue: Magnetite
Gangue: Serpentine
Gangue: Chlorite
Gangue: Sphalerite
Gangue: Apatite
Gangue: Galena
Gangue: Olivine
Gangue: Talc
Unknown: Cubanite
Unknown: Marcasite
Unknown: Silver
Comments
Comment (Reserve-Resource): PALLADIUM TO PLATINUM GRADE RATIO IS 3.5 TO 1.0 BEFORE PROCESSING AND LOSS OF 10%. PROVEN + PROBABLE ORE RESERVES, EAST BOULDER AREA, 12/31/95.
Comment (Geology): Tectonic Setting At Time Of Emplacement Of The Stillwater Complex Is Unknown. The Complex Was Emplaced Shortly After A Major Regional, Subduction-Related Magmatic Event That Culminated In Emplacement Of The 2.73-2.79 Ga Granitoid Suite In The Batholith Exposed In The Beartooth Uplift (Wooden And Others, 1991). However, There Is No Evidence That The Magmatism That Formed The Stillwater Complex Is Related To Convergent Margin Tectonics And Magmatism
Comment (Geology): Metals May Have Been Derived From Ultramafic Magma And Sulfur From Anorthositic Magma. If So, Sulfides Formed As Magmas Mixed
Comment (Exploration): THE J-M REEF DEPOSITS WERE DISCOVERED BY GEOCHEMICAL SURVEYS IN 1967, BUT THE PRESENCE OF SULFIDES WAS KNOWN IN THE 1930'S
Comment (Geology): THE J-M REEF IS 1-3 M THICK AND HAS BEEN TRACED FOR 40 KM. AGE OF STILLWATER COMPLEX IS 2,705 +/- 4 MA BASED ON U-PB SYSTEMATICS ON ZIRCON-BADDELEYITE (PREMO AND OTHERS, 1990)
Comment (Production): ONLY PRODUCER OF PGE AS PRIMARY COMMODITY IN THE CONTERMINOUS U.S. MINE REACHED MINING CAPACITY OF 1,000 TONS PER DAY IN 1990 FOR AN ANNUAL PRODUCTION RATE OF 50,000 OZ PT AND ABOUT 170,000 OZ PD (update- Boulder Creek on same unit is presently also mining PGE's)
Comment (Reserve-Resource): PALLADIUM TO PLATINUM GRADE RATIO IS 3.5 TO 1.0 BEFORE PROCESSING AND LOSS OF 10%. THESE ARE EAST BOULDER AREA RESERVES.
Comment (Economic Factors): BENEFICIATION STUDIES ARE CURRENTLY (4/81) IN PROGRESS BY RENO METALLURGY RECOVERY OF AU, NI, CU IS VERY LOW WHEN STUDIES ARE COMPLETED, RECOVERIES ARE EXPECTED TO IMPROVE.
Comment (Production): CONCENTRATE WOULD BE SHIPPED TO SUDBURY, ONTARIO, CANADA.
Comment (Reserve-Resource): ALL PLATINUM GROUP ELEMENTS ARE PRESENT AND RECOVERABLE ASSAYS ARE NOT AVAILABLE FOR IR, OS, RU.
Comment (Economic Factors): ESTIMATED DILUTION IS 20%
Comment (Geology): The Stillwater Complex Is Exposed Along The Northern Margin Of The Beartooth Uplift, One Of Several Laramide Basement-Cored Ranges That Make Up The Rocky Mountain Foreland Of South-Central Montana (Foose And Others, 1961: Kulik And Schmidt, 1988)
Comment (Identification): LISTED AS GSC ID # ISM0330 ON THE USGS JUNE 95 LIST UNDER THE NAME OF J-M REEF DEPOSIT. ALSO LISTED AS ISMI-PGE35. OTHER MAS SEQ# 0300970003. RELATED MAS SEQ# 0300970066: POSSIBLY TO 0300970031. THE STILLWATER PGM SMELTER IT MAY HAVE SOME RELATIONSHIP TO THIS PROPERTY. PREPRODUCTION YEARS BEGINNING IN 1982.
Comment (Workings): Approximately early 1990;s 2 ADITS WITH CROSSCUTS, DRIFTS, RAISES. 4,570+ FT DIAMOND DRILL CORE.
Comment (Geology): J-M REEF IS 400-450 M ABOVE BASE OF BANDED SERIES IN BASAL PART OF ANORTHOSITE I SUBZONE OF TROCTOLITE-ANORTHOSITE ZONE I. THIS COINCIDES WITH REAPPEARANCE OF OLIVINE IN CRYSTALLIZATION SEQUENCE. SULFIDES FORMED AS IMMISCIBLE LIQUID DROPS DURING EARLY STAGES OF REEF FORMATION ALONG WITH OLIVINE. STRUCTURES SIMILAR TO THE POTHOLE STRUCTURES IN THE MERENSKY REEF HAVE BEEN FOUND
References
Reference (Deposit): MANN, E.L., 1981, EXPLORATION MANAGER-MINING GROUP, JOHNS-MANVILLE CORPORATION: PERSONAL COMMUNICATION.
Reference (Deposit): PASCHALL, TARI. CITIZENS VOICE CONCERN ABOUT SMC EXPANSION. STILLWATER COUNTY NEWS. JUNE 24, 1992.
Reference (Deposit): STILLWATER COUNTY NEWS. SMC MINE EXPANSION NEARING SCHEDULE. JUNE 10, 1992.
Reference (Deposit): GREAT FALLS TRIBUNE. MINE EXPANSION DESCRIBED AS BOTH BOON, THREAT. JAN. 1, 1992.
Reference (Deposit): SEG NEWSLETTER. JAN. 1992, NO. 8, P. 23.
Reference (Deposit): SEG NEWSLETTER. NORTHERN ROCKIES: MONTANA. OCT. 1991, NO. 7. P. 17.
Reference (Deposit): U.S. BUREAU OF MINES, 1981, MINERAL COMMODITY SUMMARIES, PP 114-115.
Reference (Deposit): KILPATRICK, JAMES. MINE IN MONTANA BRINGS UP QUESTION OF ROYALTIES. LIVINGSTON ENTERPRISE. JUNE 29, 1992.
Reference (Deposit): MINING JOURNAL, LONDON, AUG. 8, 1997, VOL. 329, #8441, P128.
Reference (Deposit): THE MINING RECORD, VOL. 108, #9, FEB. 26, 1997, PP. 18,19.
Reference (Deposit): SEGERSTROM, K., AND CARLSON, R.R., U.S.G.S. OPEN FILE REPORTS 77-370, 78-704, 79-656, 80-364.
Reference (Deposit): THE MINING RECORD, VOL., 107, #49, DEC., 4, 1996, P18.
Reference (Deposit): READ, R.F., 1977, MINERAL DEVELOPMENT POTENTIAL OF THE STILLWATER COMPLEX, MONTANA, U.S.B.M. UNPUBLISHED MAS REPORT, 16P.
Reference (Deposit): MILLER, R.W., 1981, PROJECT COORDINATOR, STILLWATER PROJECT, ANACONDA COPPER COMPANY, PERSONAL COMMUNICATION
Reference (Deposit): PAGE, N.J. AND JACKSON,E.D., 1967, PRELIMINARY REPORT ON SULFIDE AND PLATINUM GROUP MINERALS IN THE CHROMITES OF THE STILLWATER COMPLEX, U.S.G.S. PROFRESSIONAL PAPER 575-D, PP D-123 - D-126.
Reference (Deposit): CHADWICK, J.R., 1980, IMPALA PLATINUM PREPARING TO PASS 1,000,000 OUNCES YEARLY, MINING WORLD, VOL 33, NO. 12, 5P.
Reference (Deposit): BENNETTS, J., MORRICE, E., AND WONG, M.M., 1981, PREPARATION OF PLATINUM-PALLADIUM FLOTATION CONCENTRATE FROM STILLWATER COMPLEX ORE, U.S.B.M. RI 8500.
Reference (Reserve-Resource): THE MINING RECORD, VOL. 108, #9, FEB. 26, 1997, PP. 18, 19.
Reference (Reserve-Resource): MONT. BUREAU OF MINES AND GEOL. BULLETIN 129, 1991, 1:500,000 SCALE.
Reference (Reserve-Resource): STILLWATER MINING COMPANY 1995 ANNUAL REPORT, PP. 13, 30.
Reference (Geology): Czamanske, G.K., and Zientek, M.L., technical editors, 1985, The Stillwater Complex, Montana: Geology and guide: Montana Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 92, 396 p.
Reference (Production): COOMBES, J.S., 1990, PLATINUM 1990: JOHNSON MATTHEY, P. 18.
Reference (Geology): BOW, C., WOLFGRAM, D., TURNER, A., BARNES, S., EVANS, J., ZDEPSKI, M., AND BOUDREAU, A., 1982, INVESTIGATIONS OF THE HOWLAND REEF OF THE STILLWATER COMPLEX, MINNEAPOLIS ADIT AREA: STRATIGRAPHY, STRUCTURE, AND MINERALIZATION: ECONOMIC GEOLOGY, V. 77, P. 1481-1492.
Reference (Geology): TODD, S.G., KEITH, D.W., LE ROY, L.W., SCHISSEL, D.J., MANN, E.L., AND IRVINE, T.N., 1982, THE J-M PLATINUM-PALLADIUM REEF OF THE STILLWATER COMPLEX, MONTANA: I. STRATIGRAPHY AND PETROLOGY: ECONOMIC GEOLOGY, V. 77, P. 1454-1480.
Reference (General): ZIENTEK, M.L., 1993, MINERAL RESOURCE APPRAISAL FOR LOCATABLE MINERALS: THE STILLWATER COMPLEX, IN HAMMARSTROM, J.M., ZIENTEK, M.L., AND ELLIOTT, J.E., EDS., MINERAL RESOURCE ASSESSMENT OF THE ABSAROKA-BEARTOOTH STUDY AREA, CUSTER AND GALLATIN NATIONAL FORESTS, MONTANA: U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OPEN-FILE REPORT 93-207, P. F1-F83.
Reference (Reserve-Resource): STILLWATER MINING COMPANY 1994 ANNUAL REPORT, P10.
Reference (Deposit): STILLWATER PGM RESOURCES, 1980, INITIAL PLAN OF OPERATIONS FOR POSSIBLE FUTURE MINING ACTIVITY BY STILLWATER PGM RESOURCES IN SWEET GRASS COUNTY, STILLWATER COMPLEX, MONTANA, 18P, 2 ILLUSTRATIONS.
Reference (Deposit): SJOBERG, J., 1981, GEOLOGIST, U.S.B.M. RENO RESEARCH CENTER: PERSONAL COMMUNICATION.
Principal Gold Districts of Montana
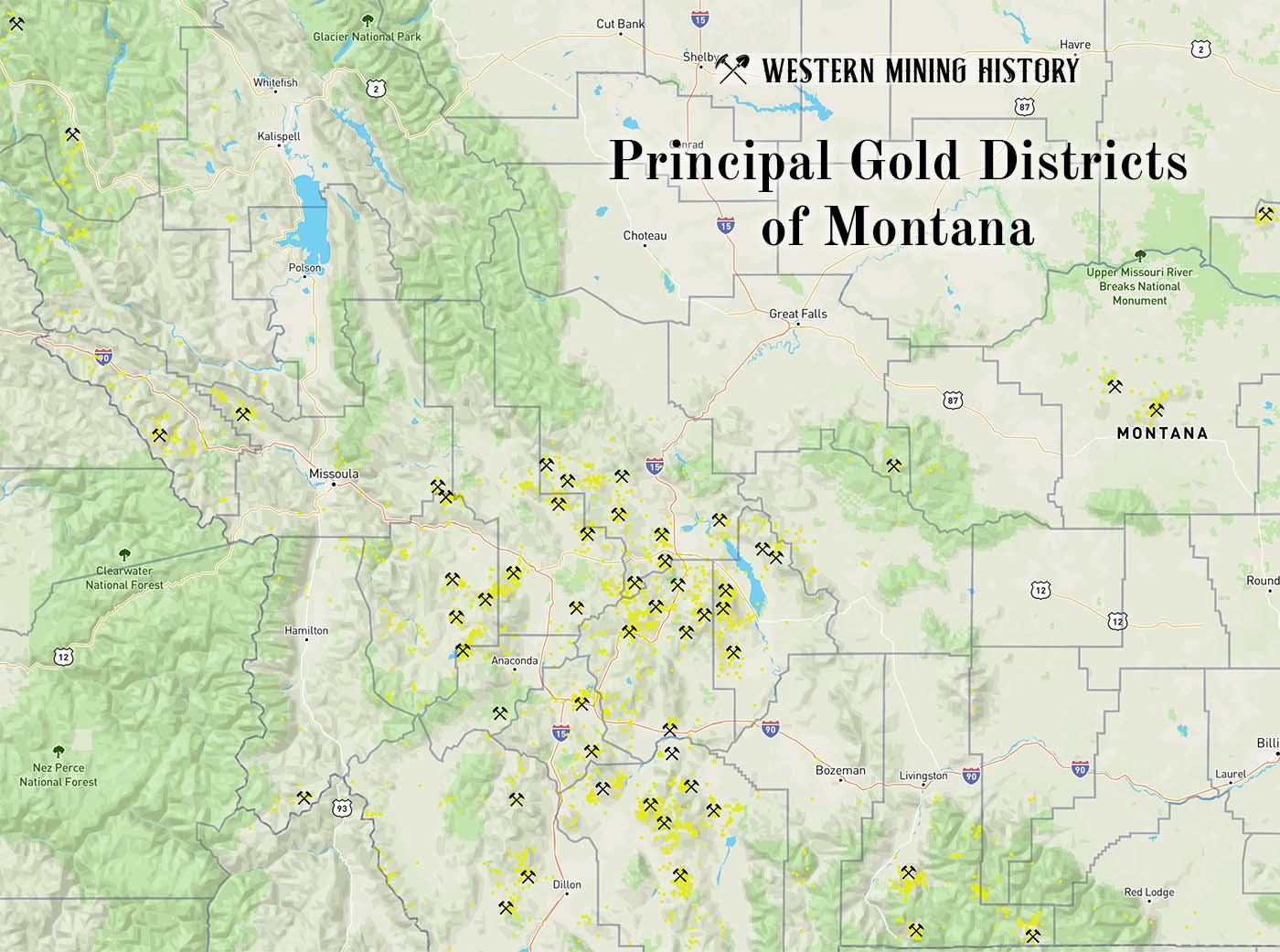
In Montana, 54 mining districts have each have produced more than 10,000 ounces of gold. The largest producers are Butte, Helena, Marysville, and Virginia City, each having produced more than one million ounces. Twenty seven other districts are each credited with between 100,000 and one million ounces of gold production. Read more: Principal Gold Districts of Montana.