The Iron Mountain Mine is a copper and zinc mine located in Shasta county, California at an elevation of 3,100 feet.
About the MRDS Data:
All mine locations were obtained from the USGS Mineral Resources Data System. The locations and other information in this database have not been verified for accuracy. It should be assumed that all mines are on private property.
Mine Info
Elevation: 3,100 Feet (945 Meters)
Commodity: Copper, Zinc
Lat, Long: 40.67556, -122.52667
Map: View on Google Maps
Iron Mountain Mine MRDS details
Site Name
Primary: Iron Mountain Mine
Commodity
Primary: Copper
Primary: Zinc
Secondary: Silver
Secondary: Iron
Secondary: Gold
Secondary: Platinum
Location
State: California
County: Shasta
District: West Shasta Copper-Zinc District
Land Status
Land ownership: Private
Note: the land ownership field only identifies whether the area the mine is in is generally on public lands like Forest Service or BLM land, or if it is in an area that is generally private property. It does not definitively identify property status, nor does it indicate claim status or whether an area is open to prospecting. Always respect private property.
Holdings
Not available
Workings
Not available
Ownership
Owner Name: Iron Mountain Mines, Inc.
Years: 1985 -
Production
Year: 1947
Time Period: 1897-1947
Material type: CU
Description: Cp_Grade: ^2-5% Zn, 7.5% Cu, 1 Oz/Ton Ag, 0.04 Oz/Ton Au
Year: 1947
Time Period: 1897-1947
Material type: CU
Description: Cp_Grade: ^3.5% Zn, 2% Cu, 1 Oz/Ton Ag, 0.02 Oz/Ton Au
Year: 1947
Time Period: 1897-1947
Material type: CU
Description: Cp_Grade: ^3.5% Cu, 0.04 Oz/Ton Ag, 0.001 Oz/Ton Au
Deposit
Record Type: Site
Operation Category: Past Producer
Operation Type: Unknown
Year First Production: 1897
Year Last Production: 1962
Discovery Year: 1865
Years of Production:
Organization:
Significant: N
Deposit Size: L
Physiography
General Physiographic Area: Pacific Mountain System
Physiographic Province: Pacific Border Province
Physiographic Section: Klamath Mountains
Mineral Deposit Model
Model Name: Massive sulfide, kuroko
Orebody
Name: BRICK FLAT
Form: LENTICULAR
Name: RICHMOND
Form: LENTICULAR
Name: MATTIE
Form: LENTICULAR
Name: HORNET
Form: LENTICULAR
Structure
Type: R
Description: Folds
Type: L
Description: Major Post-Mineral Faults Are Scott, Camden, And J Faults; The Camden Also Had Premineral Movement. Scott Fault Zone Is 3-5 Ft Wide With Many Anastomosing Slickensides And Dark-Gray To White Gouge. Scott Is A Normal Fault, Dipping 50ne, With 250 Ft Dip-Slip Displacement. Camden Fault Zone Is 50 Ft Wide At 2,600 Ft Level.
Alterations
Alteration Type: L
Alteration Text: Hydrothermal Pyritization, Silicification
Rocks
Name: Shale
Role: Associated
Age Type: Associated Rock
Age Young: Late Devonian
Name: Shale
Role: Associated
Age Type: Host Rock Unit
Age Young: Early Devonian
Name: Shale
Role: Associated
Age Type: Host Rock
Age Young: Early Devonian
Analytical Data
Not available
Materials
Ore: Covellite
Ore: Antlerite
Ore: Chalcocite
Ore: Ilmenite
Ore: Greenockite
Ore: Magnetite
Ore: Galena
Ore: Chalcopyrite
Ore: Pyrite
Ore: Hematite
Ore: Sphalerite
Ore: Malachite
Ore: Pyrrhotite
Ore: Sulfur
Gangue: Calcite
Gangue: Quartz
Comments
Comment (Location): LOCATION GIVEN IS MINE SYMBOL NEAR CENTER SEC. 34 SURROUNDED BY DUMPS
Comment (Commodity): PYRITE AND CHALCOPYRITE FOUND IN APPROXIMATELY EQUAL AMOUNTS. PLATINUM REPORTED IN SMELTER RETURNS FROM IRON MOUNTAIN (EILERS, 1913)
Comment (Production): CUMULATIVE COPPER PRODUCTION ENTRIES ARE FOR FLOTATION PLANT, COPPER ORE OF OLD MINE OREBODY, DISSEMINATED COPPER
Comment (Development): SILVER DISCOVERED IN GOSSAN IN 1879. MINED FOR SULFUR DURING LATE 1950'S TO 1962. IN 1985 IRON MOUNTAINS MINES, INC. BEGAN ENGINEERING STUDIES FOR A $20 MILLION IN-SITU MINING OPERATION DESIGNED TO RECOVER CU, ZN, AND PRECIOUS METALS
Comment (Workings): OPEN PIT
Comment (Geology): THICK COVER OF SHALE LIES STRATIGRAPHICALLY ABOVE DEPOSIT
Comment (Deposit): MASSIVE SULFIDE IS MOST ABUNDANT, DISSEMINATED CHALCOPYRITE AND QUARTZ-CHALCOPYRITE VEINS IN SCHCISTOSE ROCKS ARE LESS ABUNDANT. THERE ARE 8 MASSIVE SULFIDE BODIES IN MINE AREA; DIMENSIONS ARE FOR THE BRICK FLAT, RICHMOND, HORNET, AND MATTIE ORE BODIES ONLY. OVERALL DEPOSIT LENGTH FOR THESE ORE BODIES IS 3500 FT.
References
Reference (Deposit): KINKEL, A.R., HALL, W.E., AND ALBERS, J.P., 1956, GEOLOGY AND BASE-METAL DEPOSITS OF WEST SHASTA COPPER-ZINC DISTRICT, SHASTA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA: U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROFESSIONAL PAPER 285, P. 117-129.
Reference (Deposit): EILERS, A., 1913, RARE METALS IN BLISTER COPPER: AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF MINING ENGINEERS TRANSACTIONS, V. 47, P. 217-218.
Reference (Production): KINKEL AND OTHERS, 1956, P. 118; SEG FIELD TRIP NOTES
Reference (Reserve-Resource): SEG FIELD TRIP NOTES
Reference (Deposit): NOTES PROVIDED FOR SOCIETY OF ECONOMIC GEOLOGISTS KLAMATH MOUNTAINS FIELD TRIP, OCTOBER 7-13, 1984.
Reference (Deposit): KINKEL, A.R., AND ALBERS, J.P., 1951, GEOLOGY OF THE MASSIVE SULFIDE DEPOSITS AT IRON MOUNTAIN, SHASTA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA: CALIFORNIA DIVISION OF MINES SPECIAL REPORT 14, 19 P.
Reference (Deposit): CALIFORNIA GEOLOGY, 1986, MINERAL INDUSTRY OF CALIFORNIA, 1985: CALIFORNIA GEOLOGY, V. 39, P. 93.
California Gold
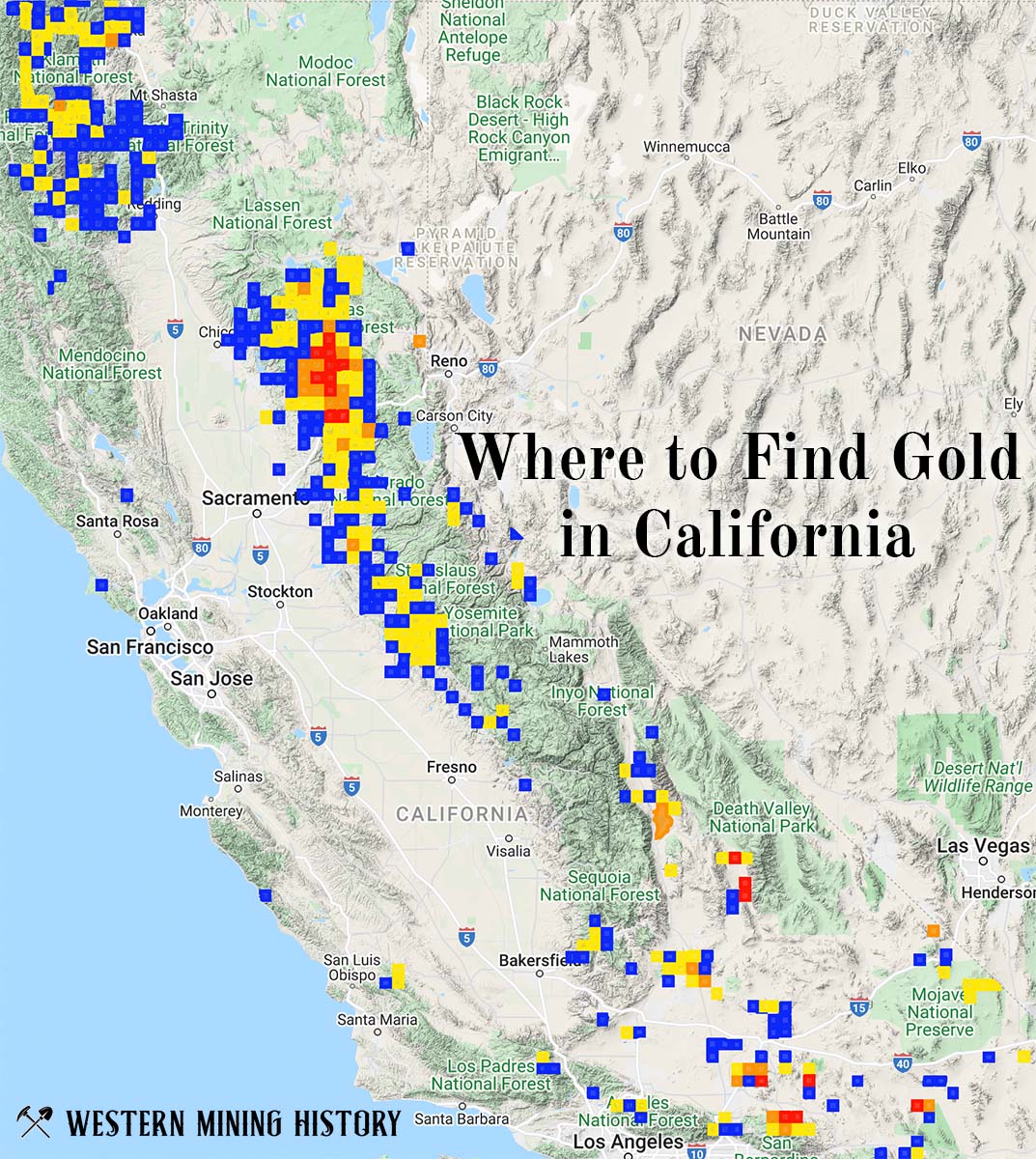
"Where to Find Gold in California" looks at the density of modern placer mining claims along with historical gold mining locations and mining district descriptions to determine areas of high gold discovery potential in California. Read more: Where to Find Gold in California.