The Fishtail Creek Ni-Cu is a copper and nickel mine located in Stillwater county, Montana at an elevation of 7,999 feet.
About the MRDS Data:
All mine locations were obtained from the USGS Mineral Resources Data System. The locations and other information in this database have not been verified for accuracy. It should be assumed that all mines are on private property.
Mine Info
Elevation: 7,999 Feet (2,438 Meters)
Commodity: Copper, Nickel
Lat, Long: 45.34028, -109.75694
Map: View on Google Maps
Fishtail Creek Ni-Cu MRDS details
Site Name
Primary: Fishtail Creek Ni-Cu
Commodity
Primary: Copper
Primary: Nickel
Secondary: Palladium
Secondary: Platinum
Secondary: Cobalt
Tertiary: PGE
Tertiary: Gold
Tertiary: Silver
Location
State: Montana
County: Stillwater
District: In Stillwater Complex
Land Status
Land ownership: National Forest
Note: the land ownership field only identifies whether the area the mine is in is generally on public lands like Forest Service or BLM land, or if it is in an area that is generally private property. It does not definitively identify property status, nor does it indicate claim status or whether an area is open to prospecting. Always respect private property.
Holdings
Not available
Workings
Not available
Ownership
Not available
Production
Not available
Deposit
Record Type: Site
Operation Category: Occurrence
Operation Type: Unknown
Years of Production:
Organization:
Significant: N
Deposit Size: S
Physiography
General Physiographic Area: Rocky Mountain System
Physiographic Province: Middle Rocky Mountains
Mineral Deposit Model
Model Name: Stillwater Ni-Cu
Orebody
Form: STRATIFORM, PODS, LENSES
Structure
Type: R
Description: The Stillwater Complex Is Exposed Along The Northern Margin Of The Beartooth Uplift, One Of Several Laramide Basement-Cored Ranges That Make Up The Rocky Mountain Foreland Of South-Central Montana (Foose And Others, 1961: Kulik And Schmidt, 1988)
Alterations
Alteration Type: L
Alteration Text: None Related To Ore-Forming Process
Rocks
Name: Quartz Monzonite
Role: Host
Age Type: Host Rock
Age Young: Early Cretaceous
Name: Quartz Monzonite
Role: Host
Age Type: Associated Rock Unit
Age Young: Neoarchean
Analytical Data
Not available
Materials
Ore: Pentlandite
Ore: Pyrrhotite
Ore: Chalcopyrite
Gangue: Magnetite
Gangue: Plagioclase
Comments
Comment (Deposit): THERE ARE 12 STRATIGRAPHIC UNITS THAT CONTAIN PGE. 4 OF THEM HAVE BEEN DEFINED BY GEOCHEMICAL SAMPLING AS CONTAINING HUNDREDS TO THOUSANDS OF PPB AU+PT+PD. MAXIMUM THICKNESS GIVEN IS FOR ZONE 2 (PMZ-2). MINERALIZATION IS STRATIFORM. NOT ENOUGH DETAIL IS GIVEN TO DETERMINE WHETHER THIS MINERALIZATION IS OF SYNOROGENIC-SYNVOLCANIC OR MERENSKY REEF TYPE. M.L. ZIENTEK SUGGESTS IT IS MORE SIMILAR TO MERENSKY REEF.
Comment (Workings): GEOCHEMICAL SAMPLING ONLY
Comment (Geology): INTRUSION IS NOT METAMORPHOSED. THERE ARE 16 CYCLIC UNITS WITHIN INTRUSION
Comment (Location): IN MEDICINE BOW NATIONAL FOREST. UTM COORDINATES ARE APPROXIMATE AND DO NOT CORRESPOND TO LAT/LONG
Comment (Location): UNSURVEYED. IN CUSTER NATIONAL FOREST; PREVIOUS QUAD DESIGNATION = EMERALD LAKE 1:24000
Comment (Deposit): DEPOSIT IS PROBABLY SIMILAR TO MOUAT
Comment (Workings): DRILLING BY ANACONDA IN 1977: 6 HOLES TOTALING 2,190 FT
Comment (Geology): AGE OF STILLWATER COMPLEX IS 2,705 +/- 4 MA BASED ON U-PB SYSTEMATICS ON ZIRCON-BADDELEYITE (PREMO AND OTHERS, 1990)
Comment (Commodity): SEE PAGE (1979) FOR GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF BASAL SERIES MINERALIZATION. NO PUBLISHED PGE DATA AVAILABLE FOR THIS AREA
References
Reference (Deposit): PAGE, N.J, AND NOKLEBERG, W.J., 1974, GEOLOGIC MAP OF THE STILLWATER COMPLEX, MONTANA: U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY MISCELLANEOUS GEOLOGIC INVESTIGATIONS MAP I-797, SCALE 1:12,000.
Reference (Deposit): PREMO, W.R., HELZ, R.T., ZIENTEK, M.L., AND LANGSTON, R.B., 1990, U-PB AND SM-ND AGES FOR THE STILLWATER COMPLEX AND ITS ASSOCIATED SILLS AND DIKES, BEARTOOTH MOUNTAINS, MONTANA: IDENTIFICATION OF A PARENT MAGMA?: GEOLOGY, V. 18, P. 1065-1068.
Reference (Deposit): PAGE, N.J, 1979, STILLWATER COMPLEX, MONTANA - STRUCTURE, MINERALOGY, AND PETROLOGY OF THE BASAL ZONE WITH EMPHASIS ON THE OCCURRENCE OF SULFIDES: U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROFESSIONAL PAPER 1038, 69 P.
Reference (Deposit): ZIENTEK, M.L., 1993, MINERAL RESOURCE APPRAISAL FOR LOCATABLE MINERALS: THE STILLWATER COMPLEX, IN HAMMARSTROM, J.M., ZIENTEK, M.L., AND ELLIOTT, J.E., EDS., MINERAL RESOURCE ASSESSMENT OF THE ABSAROKA-BEARTOOTH STUDY AREA, CUSTER AND GALLATIN NATIONAL FORESTS, MONTANA: U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OPEN-FILE REPORT 93-207, P. F1-F83.
Reference (Deposit): ZIENTEK, M.L., AND RIPLEY, E.M., 1990, SULFUR ISOTOPIC STUDIES OF THE STILLWATER COMPLEX AND ASSOCIATED ROCKS, MONTANA: ECONOMIC GEOLOGY, V. 85, P. 376-391.
Principal Gold Districts of Montana
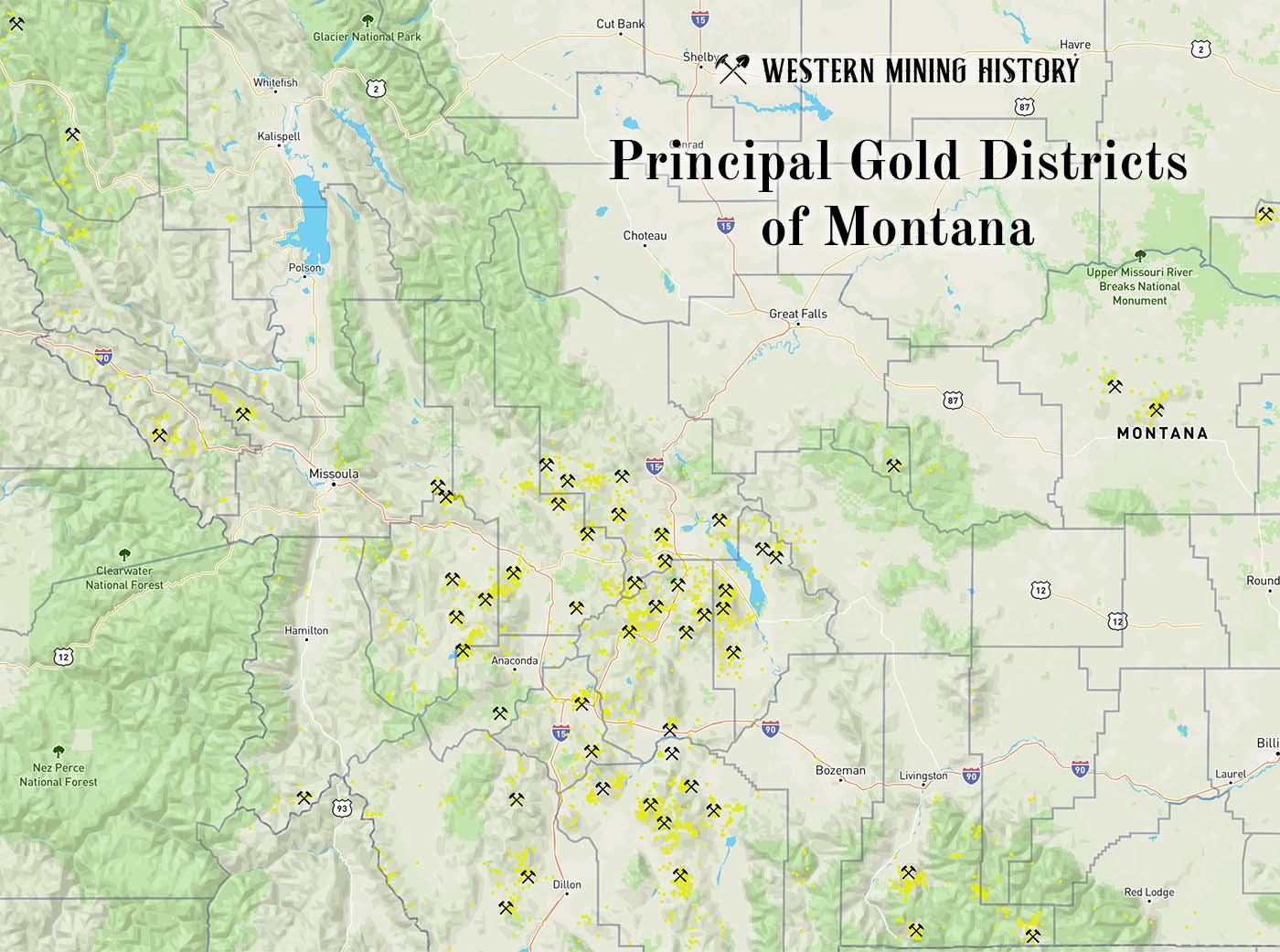
In Montana, 54 mining districts have each have produced more than 10,000 ounces of gold. The largest producers are Butte, Helena, Marysville, and Virginia City, each having produced more than one million ounces. Twenty seven other districts are each credited with between 100,000 and one million ounces of gold production. Read more: Principal Gold Districts of Montana.