The Eva May is a lead mine located in Jefferson county, Montana at an elevation of 6,719 feet.
About the MRDS Data:
All mine locations were obtained from the USGS Mineral Resources Data System. The locations and other information in this database have not been verified for accuracy. It should be assumed that all mines are on private property.
Mine Info
Elevation: 6,719 Feet (2,048 Meters)
Commodity: Lead
Lat, Long: 46.3489, -112.22470
Map: View on Google Maps
Eva May MRDS details
Site Name
Primary: Eva May
Commodity
Primary: Lead
Tertiary: Silver
Tertiary: Gold
Tertiary: Copper
Location
State: Montana
County: Jefferson
Land Status
Land ownership: National Forest
Note: the land ownership field only identifies whether the area the mine is in is generally on public lands like Forest Service or BLM land, or if it is in an area that is generally private property. It does not definitively identify property status, nor does it indicate claim status or whether an area is open to prospecting. Always respect private property.
Holdings
Not available
Workings
Not available
Ownership
Not available
Production
Not available
Deposit
Record Type: Site
Operation Category: Past Producer
Operation Type: Underground
Mining Method: Unknown
Years of Production:
Organization:
Significant: N
Physiography
General Physiographic Area: Rocky Mountain System
Physiographic Province: Northern Rocky Mountains
Mineral Deposit Model
Not available
Orebody
Not available
Structure
Not available
Alterations
Not available
Rocks
Not available
Analytical Data
Not available
Materials
Not available
Comments
Comment (Environmental Factors): THE TAILINGS MAY ERODE INTO CATACRACT CREEK DURING STORM EVENTS. THE ADIT DISCHARGE AT ADIT #2 EXCEEDED THE MAXIMUM CONTAMINANT LEVEL FOR ARSENIC AND CADMIUM. THE DISCHARGE ENTERED A SMALL DIVERSION DITCH FROM CATARACT CREEK WHICH FLOWED THROUGH THE DUMP AND THEN RETURNED TO THE CREEK. WATER SAMPLES FROM CATARACT CREEK WERE NOT COLLECTED DURING THIS INVESTIGATION DUE TO HIGH RELATIVE FLOWS. SEDIMENT SAMPLES COLLECTED FROM CATARACT CREEK DOCUMENTED OBSERVED RELEASES OF ARSENIC, COPPER, LEAD, AND ANTIMONY.
References
Reference (Deposit): BECRAFT-ETAL.
Reference (Deposit): U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROFESSIONAL PAPER 428, 1963, P. 91,
Reference (Deposit): ROBY-ETAL.
Reference (Deposit): MONTANA BUREAU OF MINES & GEOLOGY BULLTINE 16, 1960, P. 29,
Reference (Deposit): MONTANA BUREAU OF MINES & GEOLOGY MEMOIR 31, 1950, P. 43.
Reference (Deposit): PRIORITY SITES, SUMMARY REPORT, MARCH 1994, P. 5-92.
Reference (Deposit): MONTANA DEPARTMENT OF STATE LANDS. ABANDONED HARDROCK MINES
Principal Gold Districts of Montana
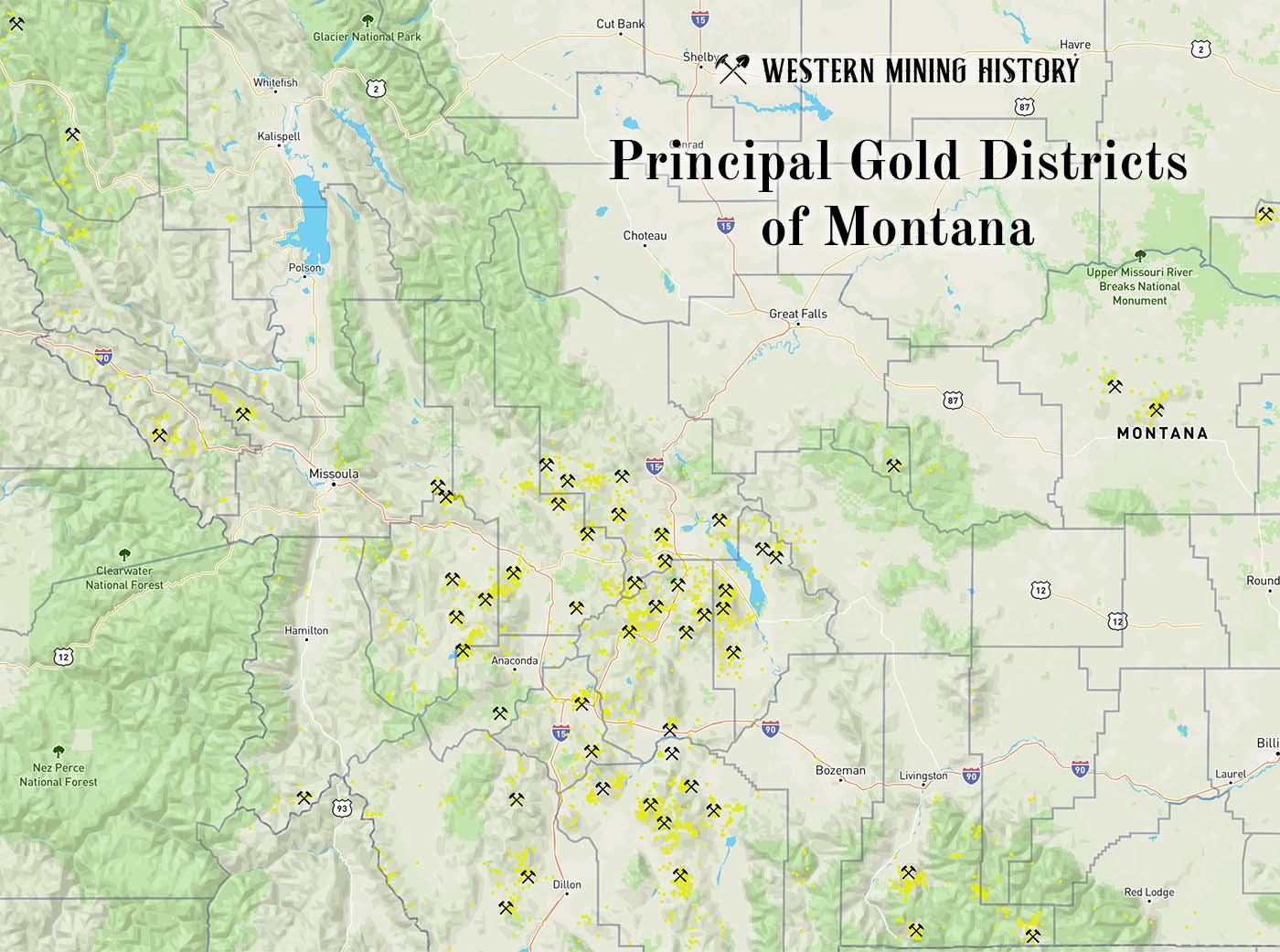
In Montana, 54 mining districts have each have produced more than 10,000 ounces of gold. The largest producers are Butte, Helena, Marysville, and Virginia City, each having produced more than one million ounces. Twenty seven other districts are each credited with between 100,000 and one million ounces of gold production. Read more: Principal Gold Districts of Montana.